In the current ecosystem, and because of their nature, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have very low liquidity. Launched in 2020, the Taker project aims to solve this problem with its liquidity protocol, based on the lending and borrowing of NFTs. Let’s discover together how Taker works and the roles of its native token, the TKR.
A problem, the lack of liquidity in the NFT market
Currently, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are experiencing a global speculative craze. However, due to their very specific nature, the usual decentralised finance (DeFi) solutions cannot be implemented in this market. This leads to major problems that put both users and automated market makers (AMMs) at risk.
In the current system, NFTs have very low liquidity. In fact, this is why most investors consider them riskier than cryptocurrency. For example, if an investor buys Bitcoin (BTC), he can very easily sell it to an order book of buyers at different prices. On the other hand, since each NFT is unique, it is much more difficult to match buyers and sellers.
Finally, it is the intrinsic nature of an NFT that is the source of this problem. Indeed, because of their uniqueness, the market for each of them is composed of a very small pool of potential buyers. For example, if you want to buy an NFT of Zidane’s goal in the 1998 World Cup final, you would not be satisfied with an NFT of any other player’s goal in a normal match.
Finally, due to the lack of buyers, the value of a non-fungible token is extremely volatile and can fall very quickly.
One solution, Taker’s loan protocol
Announced in 2020, the Taker project aims to solve the liquidity problems of non-fungible tokens. Eventually, the aim is to make them compatible with traditional decentralised finance solutions.
Indeed, thanks to its liquidity protocol, Taker will allow users to borrow stablecoin by depositing for rent all kinds of crypto-assets (including NFTs). On the flip side, lenders will be rewarded by getting a portion of a deposited asset for rent. By attracting new liquidity flows, Taker hopes that the markets, especially for NFTs, will be more fluid and user-friendly.
The Taker team has already raised $3 million in initial funding and is backed by Electric Capital, DCG, Ascentive Assets, and Dragonfly Capital. The funds raised will allow Taker to launch the final version of the protocol on several blockchains such as Ethereum, Solana, Binance Smart Chain and especially Polygon.
Lending and borrowing from NFT
The Taker protocol designs a new model for NFT lending. Due to the intrinsic nature of non-fungible tokens, they all correspond to an individual asset. In other words, they all have their own identifier, a serial number that differentiates them. As a result, it is impossible for the market to uniformly price them.
This is why Taker has decided to completely revise the method of pricing a non-fungible token. An NFT embedded in Taker’s lending protocol is inherently considered to have a value of zero. This only changes when the loan transaction is completed. It is this transaction that will define and lock in the price of this NFT. Thereafter, the individual who lent the funds becomes a temporary holder of part of the NFT and receives rewards in return through the ecosystem token, the TAI.
The TAI is an ERC-20 token that is called interest-bearing. After depositing stablecoins, a lender can receive the same amount in TAI in return. However, TAI is not linked to a fiat currency and only serves as a gateway for NFTs to enter the DeFi world. Its price thus reflects the health of the NFT market.
A cross-chain bridge
Currently, DeFi is mostly built on the Ethereum blockchain (ETH). However, for the Taker team, it is absolutely essential that quality assets deployed on other blockchains can access DeFi. This is why Taker’s protocol has developed a multi-asset, cross-chain bridge (i.e. linking several blockchains) similar to Chainsafe’s Chainbridge solution. Obviously, this bridge can also be used for the transfer of NFTs.
The Taker protocol builds inter-chain bridges to improve the efficiency of asset transfer and to enrich the horizon of possible applications. These bridges will connect various public chains, such as Ethereum, Polkadot, Near, Solana and especially Polygon. Indeed, Taker recently announced its partnership with sidechain Polygon, formerly Matic Network, with a view to building more scalable solutions to bring liquidity to the NFT markets.
Buyers of NFTs on Polygon will now have the opportunity to explore various liquidity options while investing in NFTs. In addition, Taker will introduce quality NFT assets from other blockchains for Polygon users. This partnership with Polygon will fuel Taker’s growth by bringing a wealth of new NFT projects and their strong associated communities.
Taker protocol flow chart
What is Taker DAO and its governance token used for?
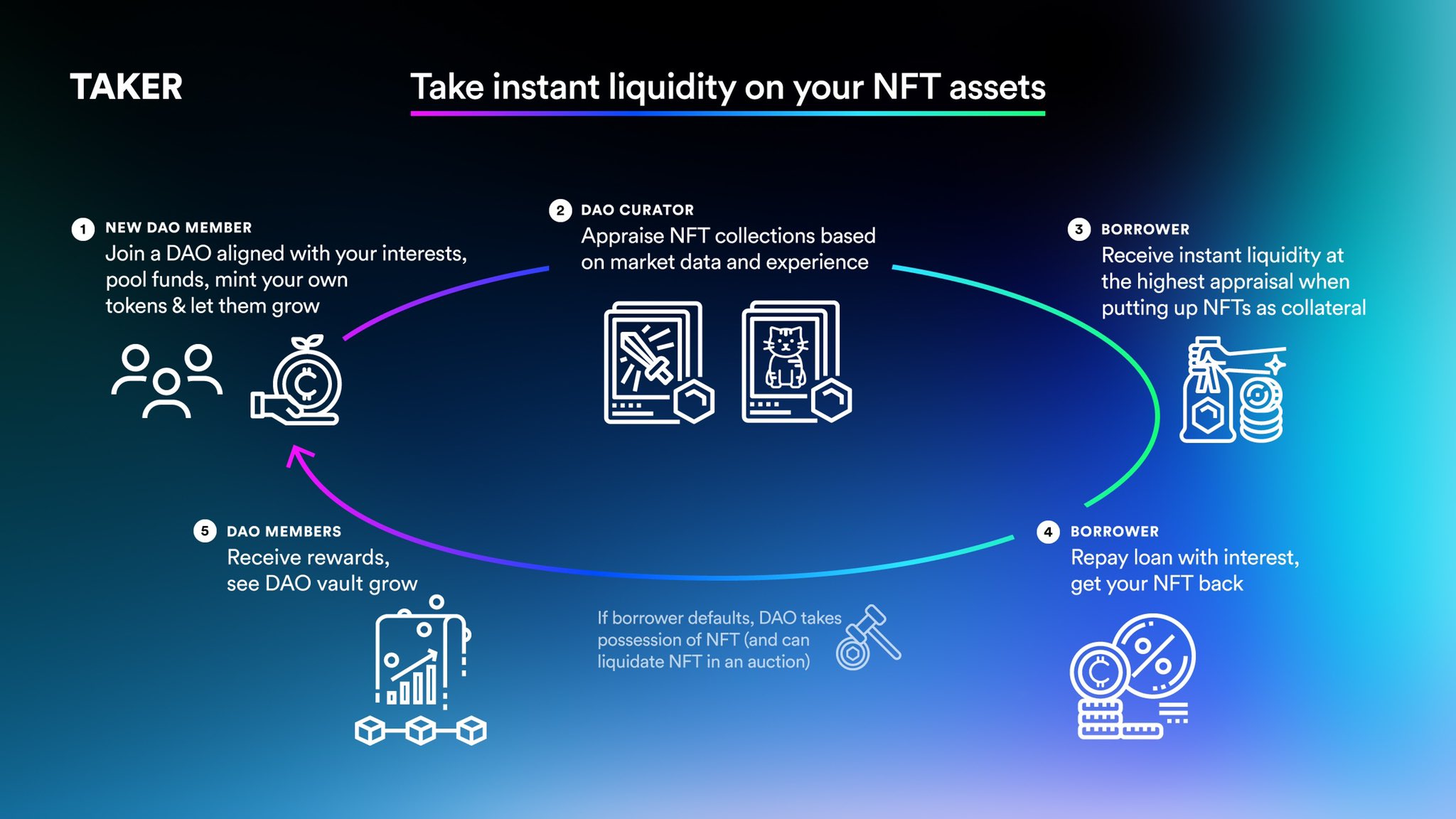
Taker DAO is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO). It represents the Taker community and will be managed by a set of TKR holders, the governance token of the project. Taker aims to “become a truly decentralised application, embodying the spirit of the blockchain”.
Taker DAO will contain numerous sub-DAOs, each of which will manage its own whitelist. This will encompass a set of NFTs and the main role of the sub-DAO will be to manage the floor price of one of these NFTs if the borrower defaults on the loan.
We believe it is best to mitigate the risks to our lenders by carefully selecting the NFT assets that our community wants and trusts the most. By aligning the interests of DAOs with those of lenders, we will mitigate risk exposure for lenders and maximise profits for DAOs,” reads one of Taker’s press releases.
In addition, each sub-DOA will have its own funds and can choose to focus exclusively on a specific type of NFT asset. For example, it could focus only on artworks or only on metaverses.
The TKR governance token will serve several purposes for its holders. Firstly, it will allow participation in the on-chain governance of the project by granting voting rights for major events.
Secondly, having a TKR will allow the holder to receive interest from the platform’s revenues. In addition, this token will give the right to modify certain parameters of the liquidity pools, notably the loan-to-value ratio, thus reducing the collateral required to take out loans. Finally, TKR holders will be able to stake their tokens to receive various rewards.
